How did you get into the bottleneck?
A growing startup commonly underinvests in its onboarding process. The
need to scale up headcount rapidly can come about unexpectedly. An event
can trigger the team scaling – perhaps the product took off with
customers, or the startup acquired a company or pivoted in a new product
direction. Quickly, plans change to how many people the startup now needs
to achieve their new goals, the recruiting team starts interviewing and
making offers. With added pressure, you don’t take time to optimize the
onboarding process. If an effective onboarding system wasn’t already in place, the
new employees are dropped into teams, assigned some tasks, and left to
figure out how to become productive for themselves. It’s particularly
problematic if team members aren’t collaboratively helping the new
employee get up to speed, there’s no onboarding documentation, the code
is impossible to read, or the product goals and KPIs unclear. Then new
employees can become lost, dissatisfied and underproductive. In this
article we will explore signs that your company is bottlenecked by an
ineffective onboarding process, and the best practice solutions we have
seen work at Thoughtworks Scaleup Studio.
In addition to onboarding new hires, the process is utilized when
reorganizing teams. The studio believe the ability to learn, fail fast and
refocus is a important skill for successful scaling. A nimble startup will
pivot as it responds to learnings and landscape changes, this involves
changing product team goals and reassigning resources to best target the
new goals. To do this easily, we need the ability for the reassigned team
members to get up to speed quickly. Most of the capabilities in this
article, will also apply to reorganizing.
Onboarding is a key business process
Onboarding is often seen as merely granting access and doing a set of
administrative tasks before handing new employees to their manager and
team. It’s not thought of as an end-to-end business process. But a
well-run onboarding process addresses social and cultural integration
and facilitates collaboration among the different functions that a new
employee has to interact with. The onboarding process typically involves
human resources, engineering management, legal, IT Operation, security,
and product team members. Spanning so many groups means it can be very
disjointed. Optimizing the process is difficult because often no one
owns the whole process, and you must bring all the different players
together.
Software leaders put a lot of effort into shaping hiring plans and
supporting recruiting efforts, but often neglect to give much thought to
how new employees will become effective. We believe this to be a
mistake, as effective onboarding acts as a “multiplier effect” for new
hires.
From a clinical perspective, what is the value of a new employee?
Without proper onboarding, new hires will only exhibit a fraction of
their value and productivity, some as low as 50%. With an ROI at this
level, you are less likely to achieve your intended goals. Leaders are
forced to do additional hiring, which will increase organization
complexity and workload for managers. To avoid this, we recommend
putting the same amount of effort into optimizing onboarding as you
would hiring new employees.
In our opinion the onboarding process doesn’t end after a week or a
month – it keeps going until the person is fully productive. As soon as
someone accepts an offer, the onboarding process begins, followed by a
robust new hire orientation, receiving of laptops and access to
appropriate systems. It continues after they join their team, as they
carry out their duties for the first time, build relationships with
their team members and managers, and develop habits around their common
tasks. The last phase of onboarding enables an employee to reach full
productivity, where they can contribute to the team creatively, teach
others and contribute back into the onboarding process. This timeline is
dependent on role, domain and complexity.
Optimal onboarding timeline
To gauge how you are doing, this table represents what we observe to
be optimal timelines for a developer onboarding. We will explain the
concepts mentioned here further in the rest of the article:
| Milestone | Completed By |
|---|---|
| Access to all HR and administrative systems | Day one |
| Access to workstation and personal development environment is setup with necessary tools |
Day one |
| Company mission and business goals are explained and discussed |
Day two |
| Complete a push to production for a trivial change, assisted by peer |
Day three |
| Manager has set expectations with employee and given them an OKR |
Week one |
| Paired with colleague on developing a real feature all the way to production and performed defect resolution |
Week two |
| Understood key customer problems and internal operation processes |
Week two |
| Developer: Able to be an “Anchor” on a story | Week 3 – 5† |
| Developer: Able to lead support calls | Week 5 – 7† |
† depending on complexity and experience
Signs you are approaching a scaling bottleneck
New people cannot access tools and systems
Most new joinees usually come with a sense of excitement and
anticipation about their new assignment, eager to prove themselves in
their new environment. Having to wait for access to basic resources like
the work laptop, source control, team documentation portals, test
environments, software licenses, etc. can dampen the spirits of even the
most enthusiastic candidates. Not knowing which systems to get access to
and having to chase specific individuals to find out how can be very
frustrating.
To spot these delays you can monitor the steps new employees are
taking. Keep an eye on the number of tickets opened and the amount of
time it takes to resolve these tickets.
New developers cannot make a production deployment
A quantifiable metric to use is how long it takes a new employee
to write code, commit and deploy all the way to production. This
should happen in the first week– ideally the first couple of days. It
doesn’t have to be a complex task, it can be something very trivial.
This metric is an indicator that the developer has their computer and
development environment set up correctly and has everything they need to
push to production independently. We find situations where a new
developer has been in the company weeks or even months, and has not
deployed anything to production.
Newcomers feel orphaned
Especially at startups, most managers are laser-focused on new
initiatives, and they have more work than they can handle. It’s easy
to deprioritize integrating and bringing direct reports up to speed. New
employees are left to figure out things on their own; learning systems,
forming relationships, and how to get access to resources they need.
Worse if they haven’t been given a clear goal, they may end up working
on the wrong thing. The employee becomes an orphan, resulting in much
lower productivity or quick attrition. Cultural problems like this are
hard to spot. We recommend listening to your managers and feedback from
new employees. Exit interviews are also valuable data.
Too much focus on individual work
When a startup scales by adding new employees, this can trigger a
different mode of operation. It was a small team that built the initial
product and technology platform. Each engineer was focused on building
and supporting a part of the application, likely by themselves. With the
expansion into a larger team, a problem we often observe is the tenured
employees aren’t dedicating enough time to onboarding the new employees
– collaborating and pairing with new engineers, documenting how they
work and explaining the reasons for technical decisions, etc. This makes
onboarding very difficult.
With the expanded team size, objectives should not only focus on
individual contributions, but should include how the product team as a whole is
performing. When retrospecting the product team should ideally look for
opportunities to help new hires become more productive. An anti-pattern
we see is planning with individuals allocated to streams of work by
themselves, as this removes the opportunity to transfer knowledge.
Not enough openness to change
When you hire new employees, they likely come with different
experiences than the existing team (especially if you are hiring outside
of your personal network). They’ll have different opinions and
viewpoints. Too often we see companies not taking advantage of this. A
typical situation is that the startup likely has a team of “old hands”
that have found a way to work, have their own idiosyncrasies, and there
is a history to every decision. The team is dogmatic in its approaches
and shoots down the new ideas of the newcomer. This leaves the new hire
feeling unempowered, and not appreciated.
Again this is cultural and hard to spot, but some anti-patterns to
look out for are:
- Current employees hogging the meeting, talking quickly, or not
giving enough time for new employees to contribute or clarify. - Being overly protective of the status quo; shooting down ideas –
“we tried that”, “it could never work here…”. - Back-channeling through unofficial channels; tenured employees
might get work done through their established network doing them a
“favor”, rather than through a documented process.
Seemingly simple things take too long
The effectiveness of your development environment for common tasks
will be exposed when onboarding new employees. The friction may have
already been felt by existing employees, but adding more magnifies the
problem. Each new employee will have to learn how to solve common
problems and discover workarounds. Examples might be flaky automated
tests, inaccurate documentation, slow personal dev environment,
environments that are out of date, or a slow dogmatic code review
process. We can monitor some of these things by tracking low level
metrics (e.g. CI build time, PR review time, unit test run time) and
tech debt items that teams are highlighting as friction.
Fast turnover
Turnover rate of newcomers is a lagging indicator. There might be
many reasons for a high turnover rate. However it’s worth
investigating. It could be related to your onboarding process. It could
be that your new employees aren’t being properly trained, and welcomed
in the company. Your team should monitor the rate and how it’s
trending, supplement with surveys after 6 months and a year for new
employees. You can then use the learnings to improve the onboarding
process continually.
Documentation can’t answer questions from new hires
New hires, especially lateral hires, usually know what needs to be
done at a high level. However, idiosyncrasies of the new environment can
get in the way of completing even mundane tasks. For example, not
knowing the location of the source repositories or the base URL to the
integration test environment. Well-structured onboarding documentation
can help boost productivity, build confidence and generally provide a
pleasant working experience. To continuously improve and keep the
documentation up to date, new hires should be encouraged to find bugs in
it and fix them.
How do you get out of the bottleneck?
When you are thinking about designing your onboarding process it’s a
good first step to think holistically about employee effectiveness. In
the following solutions section we will describe how to create a path
to effectiveness, an example of onboarding optimization applied at
Checkr, and then some techniques we view as important.
Create a path to effectiveness
In maximizing developer effectiveness
Tim talked about the idea of focusing on outcomes rather than outputs,
and how engaged employees can create the most value for your business
and your customer. Empowered employees aren’t simply coding a
requirement, designing to a spec, or creating features based on requests
from a sales team. They’re thinking creatively about the problem space,
coming up with cost efficient, scalable and innovative solutions. Let’s
look at what an empowered employee needs, and how onboarding might enable
it:
Need
How onboarding enables it
Clear view of the company mission and business goals
Leaders
should build excitement for the mission, outlining what led to its
creation, what the future might hold, and how an employee can
contribute to that. This should include a view of the current product
strategy.
How does the company make money (or intend to)?
To instill a business sense and a focus on frugality, new employees
should know how the company currently charges for their services, its
profitability, and its level of investment.
Empathy for the customer’s experience
Set an expectation for all
employees to think about the customer. We can emphasize this by a
number of activities – observing the customer using the system, using
the system as a customer (if possible), and reading prior research
into customer problems.
An understanding for internal operations
Most software systems
have different users (beyond the target customer). It’s important to
understand all of those aspects, so that technologists can design
solutions that make those internal users efficient. This is
particularly important at scale
Business domain understanding
Many business domains are quite
complex. Understanding happens over time, but we can start with
overviews from an expert, and suggested readings
Working relationship with their team
In order to have open
conversations about concerns and ideas new hires need a level of
familiarity and vulnerability with their peers and manager. Onboarding
should include activities to enable this. It’s more difficult to do
remotely, so we recommend teams getting together in person within the
first few months of a new hire joining.
Clear understanding of their objectives
An empowered employee
needs a purpose, they need to know what their company would like them
to achieve, and how they’ll be assessed towards that
Current team topologies
The new hire should have a clear
understanding of the ownership of products and systems and whom they
can talk to get information. An up-to-date org chart with where they
sit in it’s essential. Intentionally setting up some 1:1s during the
first weeks is a good way to encourage communication across teams and
functions.
How technology is leveraged
Every startup uses technology to
innovate and scale, so all employees should have a base level of
understanding. We don’t believe it’s effective to divide roles into
‘technical’ and ‘non-technical’; some roles are just ‘more technical’
than others.
There will be role-specific needs. A developer needs know how to:
Need
How onboarding enables it
Write code and push to production
An environment that’s
fully setup and working, with access to deploy, they’re able to do it
independently. The environment gives them confidence that it will find
quality problems, and allow them to rollback safely.
Debug and fix production problems
Access to clear observability
that spans systems. This should include documentation, runbooks and
walkthrough videos of typical tasks.
Understand existing code, architecture, and
dependencies
Effective knowledge management system, access to all source code
repositories, access to dependent teams and knowledge transfer with
teammates and SMEs
.
Measure the progress of their solutions
Business and product
analytics, and also technical metrics (performance, availability,
cost, quality measures). It should include ability to experiment with
solutions (prototypes, A/B tests) and access to qualitative
feedback.
While this article is mostly aimed at developers, we can expand the
concepts into other roles. A product manager might need:
Need
How onboarding enables it
First-hand experience with customers
Start with an introduction
to key customers. Also, product managers need the space to build
relationships; we sometimes find that the founder wants to be the
conduit, which can make it difficult to get unfiltered
information.
Articulate current product strategy
A new product manager should
be able to quickly understand the current strategy, the relevant
signals, what the current product bets are, and if they’re
succeeding.
Find and access analytics
Ideally this is self-service and
exploratory, rather than having to request reports. This includes
product, behavioral, financial, marketing and sales metrics, and
system performance metrics.
Learn from previous bets and inflection points
The product is
currently designed a specific way for a number of specific reasons
(which may not be obvious). In order to successfully evolve the
product, it helps to know why it’s the way it is.
Build experiment prototypes and “play around” in the
system
Often product managers don’t have the access they need to use demo
environments or the resources to create prototypes
.
A designer might need to know how to:
Need
How onboarding enables it
Access tooling to create lo-fi and hi-fi assets
In addition to
the polished product, a designer should be able to easily create
clickable prototypes, and be able to conduct user testing with them
without much ceremony.
Find and use branding guidelines and design systems
To ensure
consistency and make designing and implementing UIs easier, these
should be accessible and well documented. The maturity of these
systems will depend on the maturity of the startup, evolving from a
shared design file to a living component library.
Discover previous user research
Recordings of previous user
testing, interview documentation, and synthesized research output
should be accessible and stored in a company knowledge base rather
than in personal silos.
Perform A/B tests and access behavioral analytics
The user
interface should be instrumented so that a designer can get as much
insight as possible in a self-service way. A number of A/B testing
frameworks allow for independent release and analysis without
developer support for certain types of changes.
This list is an example and not intended to be exhaustive; we suggest
you look at the objectives and the “jobs to be done” for your roles in
the context of your company.
To illustrate how this works in reality, we are going to use the
example of Checkr
Case Study: Checkr
Checkr, an HR technology company
powering the future of work, partnered with Thoughtworks on
scaling between 2018-2020. While working on their architecture, quality
and platform engineering, Thoughtworks consultants noticed the
effectiveness of Checkr’s onboarding process. When Checkr grew beyond
the initial team, they invested in creating a structured onboarding
process for all employees. The process was designed to build empathy for
their customers, understand the business, and bring employees to
productivity as quickly as possible. Regarded as a critical capability
by Checkr leadership, their onboarding process allowed them to grow from
30 to 300 engineering staff. Despite their success, Checkr continues to
evolve the process as they collect feedback, and try new ideas.
Cross-functional onboarding week to understand the mission, and
build empathy
Each month, Checkr ran a week-long onboarding “bootcamp” for all
new employees. The goal of the bootcamp was to provide employees a
holistic understanding of the company and product by hearing from
leadership and from other teams across Checkr. Members from other
functions such as customer success, finance, product and engineering
would review team processes and product use cases with the new
employees.
Along with the cross functional overviews, new employees were given
further opportunities to build customer empathy and understand the
problem space that Checkr aimed to solve. New employees would go to
the local courthouse to pull a record as part of a customer’s
background check and sit in on a customer support call as the customer
success representative used Checkr’s tools.
Initially, cohorts were around 20 people but grew over time. An
additional benefit of the bootcamp was that new employees quickly
built an internal network. Checkr’s Director of Engineering Krista
Moroder said: “I still use the initial network I made – one of my
onboarding buddies is still one of my first points of contact in the
Legal department.”
After the bootcamp, they conducted a role-specific 2-day workshop
followed by onboarding to their respective teams.
Path to productivity for a developer
The employee would have access to all the services and tools they
need from day one. Engineers can set up their personal development
environment with a script in a few hours. Checkr has a stated goal
that a new employee should deploy on day one, but in actuality it
changes team by team, on average it’s within the first week. They’re
currently moving from a laptop-based developer environment to a cloud
based approach, with the aim to speed up onboarding, because of the
added capacity and easier configuration management.
A lot of teams will use pair programming, which means a new
employee can jump straight into pairing on whatever task is the focus.
Krista talked about pair programming
“Thoughtworks was the catalyst for the pair programming on the team
I originally led. The primary motivation was to reduce quality
defects, reduce context switching, increase shared knowledge, improve
cycle time, and keep people connected and engaged when we went
full-remote during the pandemic. Teams use a model where engineers
choose pairs for the day when the daily standup ends.”
At Checkr they use a “you build you run it” approach, where each
developer is expected to support the systems their teams own. To learn
how to do this, after 1-2 months of joining, a new developer will
start by co-piloting the on-call support with a colleague. They can
typically resolve a problem independently after 2 months for an
internal product, or 3-6 months for a consumer product, depending on
seniority. For Krista “a productivity indicator is that their manager
or a tenured developer trusts the new developer to solve complex
issues end to end.”
Quality Awards and Learning Weeks
Onboarding is partly about the activities that happen when someone
joins, it’s also about the creating a culture that leads people to
effectiveness. Checkr wanted to encourage a continuous learning
culture, the company has run participant-led “Learning Weeks” 2-3
times a year, each time with the intention to focus on a different
capability, like infrastructure or quality, for a week. Surveys are
run before the camps, to understand current gaps in knowledge. These
weeks provide a chance to learn from peers. In an ideal world,
everyone would share expertise continually. But in a busy startup,
that doesn’t always happen. Learning Weeks set the intention, and
helps people become comfortable with asking for help and sharing
knowledge.
An important part of Checkr’s regular all hands is the Quality
Awards, where individuals are nominated by their peers and recognized
for their contributions. Instead of just celebrating typical
milestones like product launches, people are recognized for excellence
in documentation, testing, deprecation and refactoring. This
emphasizes a culture of building excitement around high technical
quality, and of peer support.
Beyond the initial onboarding period, the team sends surveys
regularly to assess the whole process. This helps them monitor whether
their processes are effective and have set a foundation for success in
the company.
Include new hires in the company culture
Bringing in new people to a startup carries the opportunity for
greater diversity in thoughts and ideas. The experience and knowledge of
new hires will make our products better, technologies more innovative
and processes more efficient. To be able to really leverage those new
hires does require work from the current team to integrate them
properly. It’s difficult for a new hire to connect and contribute to
the existing team without the right environment. The existing social
capital and prestige of the existing team is intimidating. If we can
encourage the new employees’ voices, they’ll be able to speak up and
suggest new ideas without fear of being shot down.
Creating this safe and vulnerable space is difficult. From day one,
starting with new hire orientation, the new employee should feel like
they’re part of the company’s mission and can contribute to its
evolution. Leaders can start by setting an example in how they interact
and set the principles of the company. It’ll come down to individual
interactions. We recommend instilling a culture of being mindful to
others, being aware of how others are acting and feeling, especially
during the onboarding period.
Nail the post-offer and first-day experience
It’s said that you never get a second chance to make a first
impression, and this certainly applies to onboarding. Onboarding starts
with the first interview. The way interviewers interact with candidates
will begin to set a precedent for how they perceive the company’s
culture and how they should behave. From then on, the experiences on the
first day, first week, first month and beyond matter and will have a
tremendous influence on whether they’ll succeed and be happy.
Therefore, the time leading up to the first day of employment can be
very critical. Once the candidate accepts the offer, make sure that
there’s a clear point of contact (preferably an email group instead of
an individual) for the new employee to seek clarification.
All the tools an employee needs should be available via self-service
and accessible on day one. No one wants to spend the first few weeks
playing “whack-a-mole” creating tickets for all the permissions they
need – This includes having IT systems that auto-enroll employees with
benefits, performance tracking, payroll and knowledge repositories.
An onboarding checklist can be a useful way to guide employees on
their first day. For example, at Thoughtworks new hires are given their
own Trello board with onboarding tasks. All tasks have step-by-step
instructions and contact information for further assistance, and are
prioritized in the order they should be completed. This gives new hires
a ready reckoner to complete basic tasks like setting up direct deposits
to their salary account, and also more complex ones like setting up
their work laptop. In addition, it allows them to track how they’re
progressing against common tasks all on their own and how to seek out
help.
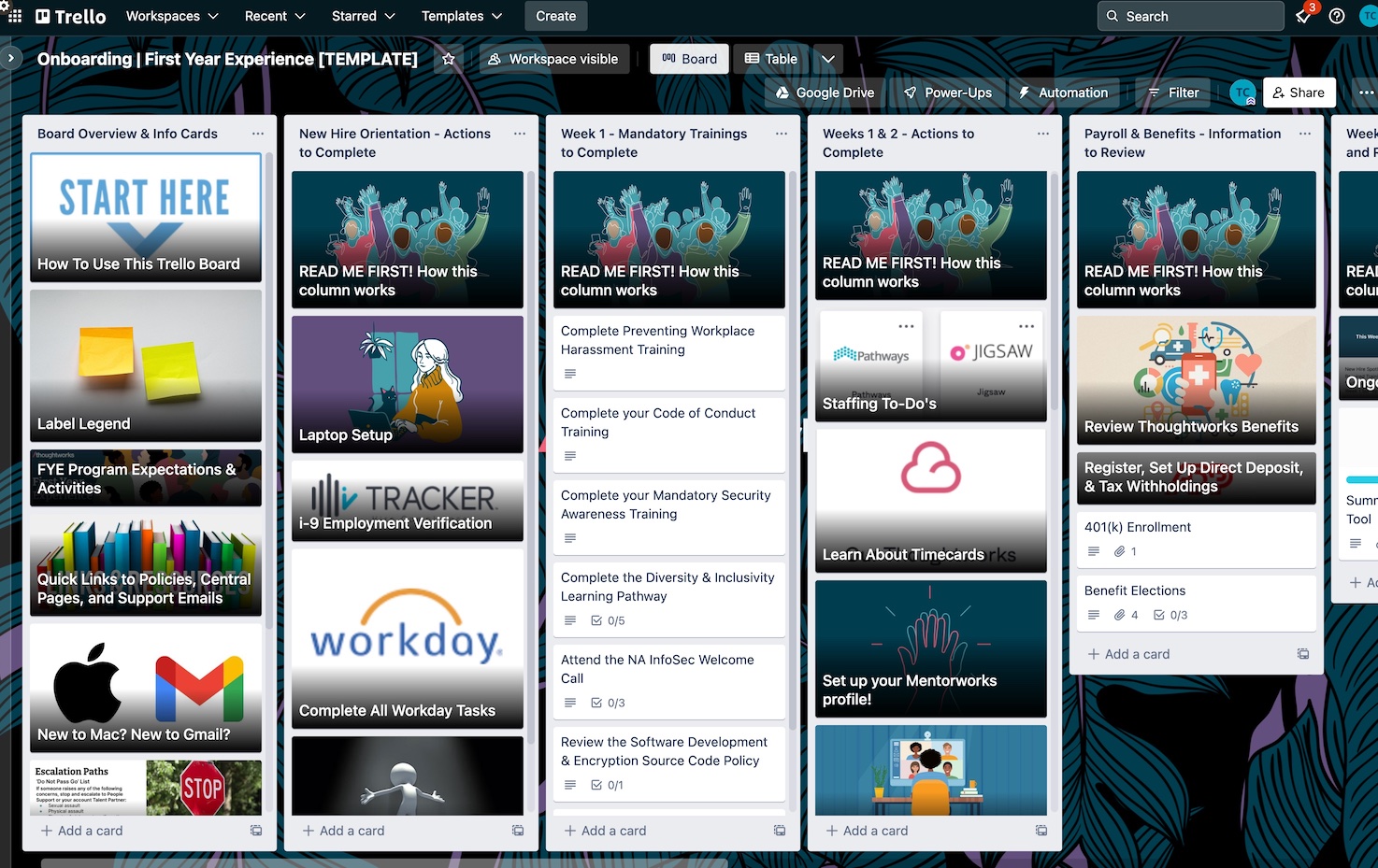
Figure 1: Thoughtworks’ onboarding checklist
New hires are assigned an onboarding buddy to help them through it.
To make this even more seamless, we have a “First Year Experience” chat
group where new and seasoned employees alike pose questions and get
help. It’s not uncommon for even long-tenured employees to continue
using it for several months after they join and is quoted as one of the
most liked aspects of the overall onboarding process.
Invest in self-service knowledge management
It’s surprising how much proprietary knowledge can be quickly
accumulated. Ideas or approaches might be well understood from earlier
sessions, but never written down. If we don’t take the time to document
things, it can make the first months frustrating for new employees. We
subscribe to the agile principle of “Working software over comprehensive
documentation”; software code should be readable but there’s still a
need for some targeted documentation. Best practices include:
- Up-to-date succinct technical documentation around libraries, API,
dependencies and integrations – A feedback loop to the technical
owners dramatically improves the usefulness and freshness of
documentation. - A taxonomy and a central search for documentation, to minimize the
amount of time to find information - Shared principles and practices: an understanding of how a team
typically operates helps a new employee adjust to a new culture. - A record of historical technical and product decisions allows for
greater context behind thought processes. - Write-up of post-mortems of degradation of service. All problems
are learning opportunities, and documenting the problem and mitigation
helps avoid future problems.
Thoughtworks’ Sensible Defaults
Over the years, Thoughtworks has accumulated a set of practices,
patterns, guidelines and a collection of general good advice that has
made us successful. Localized design-making and autonomy is key to
Thoughtworks’ culture, but we wanted to provide a “paved road” for
lateral employees to start from. This includes defaults for various
faculties such as developers, architects, business analysts, product
managers, program managers, and executive stakeholders. Each of these
also have their respective chat, email groups and communities where
anyone can ask questions, solicit feedback, share ideas and challenge
the status quo.
The development sensible defaults include a documentation around a
number of key practices. Some examples include
Frequent and continuous integration
Test Driven Development (TDD)
Pair development
Build security in
Fast and verified automated build
Automated deployment pipeline
Early and continuous deployment
Quality and debt effectively managed
Build for production
Fast Feedback
Fast feedback means being able to find out whether a change has been
successful in moments not days. It might be that unit tests have passed,
or that we haven’t broken production, or that a customer is happy with
what we’ve built.
Repeatability
Repeatability is the confidence and predictability that comes from
removing manual tasks that introduce weird inconsistencies. We also want
to spend time on activities that are more important than troubleshooting
something that should have just worked
Simplicity
We want software that contains no more complexity than it needs to do
a good job. We build for what we need now, not what we think might be
coming. But we make choices that allow our software to rapidly change to
meet the requirements that are coming.
↑ Deployment Frequency
↓ MTTR
↓ Lead Time for changes
↓ Deployment Frequency
Pair programming as a critical onboarding technique
Thoughtworks teams often earn praise from our client stakeholders for
how fast we can get up to speed to work on existing code, and quickly
learn the business domain. The (not-so) secret to this is Pair Programming, Thoughtworks loosely follows
Extreme Programming techniques adapted to the client
context, pairing is a key technique.
When we onboard a new member to the team they’ll spend
time with the product manager to learn the product goals and business
context. They’ll then start pair programming with existing members of
the team straight away, on building real functionality. To learn other
areas of the code base they’ll rotate through different members of the
team on different stories.
From our startup project experience, we find pair programming during
onboarding accelerates knowledge transfer and introduces a learning
culture. Other advantages are that it creates team norms on code style
and quality, builds trust and vulnerability between team mates, and
creates a collective code ownership. While you can achieve these things
in other ways, pair programming in our opinion is the fastest and most
effective way. These techniques can also be applied to other disciplines
e.g. pairing on design, product strategy and management.
Personal Environment Setup
It’s not enough to give a developer a set of installation
instructions to set up the environment and have them figure it out.
Ideally the personal environment should have everything the developer
needs to deploy to production and to be able to debug. It should either
be pre-installed or installed via a few operations. The first week is a
good time for a manager or teammate to pair on performing the first
deployment. Pairing this way means they get to build relationships and
they can see the friction a new employee experiences. A good practice is
doing a trivial task, to demonstrate that the environment and deployment
pipelines work. For example, Etsy uses deploying your photo to their
team page as an onboarding task.
Depending on your environment, it might be created with a
company-wide image or script, with some customization for your team and
department. Typically the most effective way is for the developer to
have a functionally equivalent copy of production with synthetic or
obfuscated data. As a team grows, the environment likely becomes too
complex and expensive to give every developer a copy; at that point the
personal environment should be based on the services and UIs of the
business domain where the team works.
The location of the personal environment might be the user’s laptop
or a cloud environment. The decision is based on a number of factors–
speed of development being the most important, but environmental
differences, privacy, and compliance are other factors. Our teams have
found that if you are using a lot of cloud services (e.g. functions as a
service), it might be better to run your personal environment in
the cloud using the real services, rather than using development
versions locally or stubs. It’s a trade-off the team will have to
decide. Keeping everything away from personal laptops also helps with data
security.
Remove friction from the onboarding process
Friction in the onboarding process is defined as anything needless an
employee has to do, or any process that is unnecessarily slow or
bureaucratic. One team can’t wholly own onboarding – it’s not a single
process. Onboarding needs intense partnership and buy-in among your HR,
recruiting, IT, learning and development, leadership, recruiting and
team peers. Many people with specific responsibilities across the
organization need to play their part in the process.
We’ve found the details matter here – you can include things like an
automated survey they get at the end of their first week or a script
that auto-assigns mandatory training in the learning management system.
The more you automate, the more you can guarantee what the new hire
experience will look like. However, not everything can be automated, and
there needs to be a clearly defined process where everyone knows their
part of the process.
Continuously Improving the process
Onboarding is a cross functional activity with many stakeholders.
Generally, there’s a need to centrally coordinate across these
functions to create a unified message and consistent experience. At
Thoughtworks, we have a First Year Experience team comprised of
operations team members dedicated part-time to creating and executing
effective onboarding experiences. They’re both the stewards of the
content – ensuring key messages stay aligned with current business
direction – but also facilitate orientation and other onboarding
activities. For a smaller startup, this coordination and execution
could be managed as a part-time responsibility of a manager from the
operations department.
As we have previously mentioned in our product vs engineering article, the value of
functional managers operating as a team to achieve a holistic outcome
also applies to the onboarding process. If you are about to ramp up
soon or you have had indicators that onboarding is not effective, we
recommend creating a working group to focus on the process and
optimizing. Figuring out the process and content will have the added
benefit of giving you better clarity into what you’re doing.
There are distinct parts that should be owned. Making sure your new
employees understand the vision is part of the leadership and often
the founder’s responsibility. With scale it would be codified. In any
case, the founder should still find ways to personally remind folks of
the mission. Creating the new hire bootcamp or setting the first week
experience, would involve a lot of different participants, but run by
someone from operations (the co-ordinator).
To continuously improve, someone should be responsible for
capturing and dispersing feedback – if some documentation isn’t clear,
or if a system isn’t fully self-serve, those improvement tasks need to
be tracked and completed, and this would likely be managed by the
“co-ordinator”. Feedback can be gathered through surveys from new
hires (we recommend surveys after 3-6 months) and from canvassing
opinions from the line managers that are incorporating new hires into
their teams.
A trap we often see when removing friction is “papering over the
cracks”. If something is proving difficult to newcomers, remember to
look for a root cause. For example, if an architecture is hard to
understand it could be that it’s documented badly, or it might be
fragmented or overly complicated.
In addition to qualitative feedback there are some quantitative
measures (mentioned in the signs section) that are useful. These are
mostly going to be output based: Can the new employees use the tools
and complete the jobs required of them? These aren’t going to tell you
much about the value they’re creating for the customer or the quality
of the code or design, but nevertheless they can help to spot friction
in the process and environment. It’s better to use these metrics as
aggregates for your engineering organization, and to track trends over
time, rather than for individual performance:
- Time to first commit to production
- When does an employee go on-call by themselves
- Time to 10th valuable commit
- First customer interview for a product manager
- First validated experiment by a designer
Investing into the onboarding process
Phase 1
Experimenting
A small close knit team, no need for a formal onboarding process
Record product and technical designs, useful for future employee understanding
Phase 2
Getting Traction
Creation of an onboarding program, by a cross-functional team led by operations
Automate workstations setup, environment creation, creates CD pipelines.
Establish self-serve knowledge management approach encompassing tech, product and business
Create sensisble default practises
Phase 3
(Hyper) Growth
Establish processes around laptop procurement, employee feedback, exit interviews, automatic onboarding to HR systems.
Implement continuous improvement program to empower teams to remove day to day friction
Platform team dedicated to developer experience, KPIs includes time to first deploy
Phase 4
Optimizing
Dedicated staff to handle onboarding process and it’s continual optimization.
Consolidate disparate bodies of knowledge
Continued leadership involvement in onboarding, to inspire new hiring batches




